Parker Solar Probe Story
wonderful journey to the sun
Scroll To Read

When reaching the sun was a methodology
The myth of Icarus is a tragic story of hubris and complacency. Icarus, the son of master craftsman Daedalus, attempted to escape from the Island of Crete by means of wings his father had constructed from feathers and wax. Daedalus warned his son not to fly too close to the sun, as the heat would melt the wax holding the feathers in place. However, Icarus became complacent and flew too close to the sun, causing his wings to melt and he to fall into the sea and drown
The myth gave rise to the idiom: "Don't fly too close to the sun" This was back then when no human-made object could touch the sun
but today we say:"Make it towards the sun"





Creation
Parker Solar Probe is built to withstand the harsh conditions and temperature fluctuations of the mission. The key lies in its custom heat shield and an autonomous independent system that helps protect the mission from the Sun’s intense light emission.Parker Solar Probe makes use of a heat shield known as the Thermal Protection System, or TPS.The TPS was built at Carbon-Carbon Advanced Technologies, using a carbon composite foam sandwiched between two carbon plates.
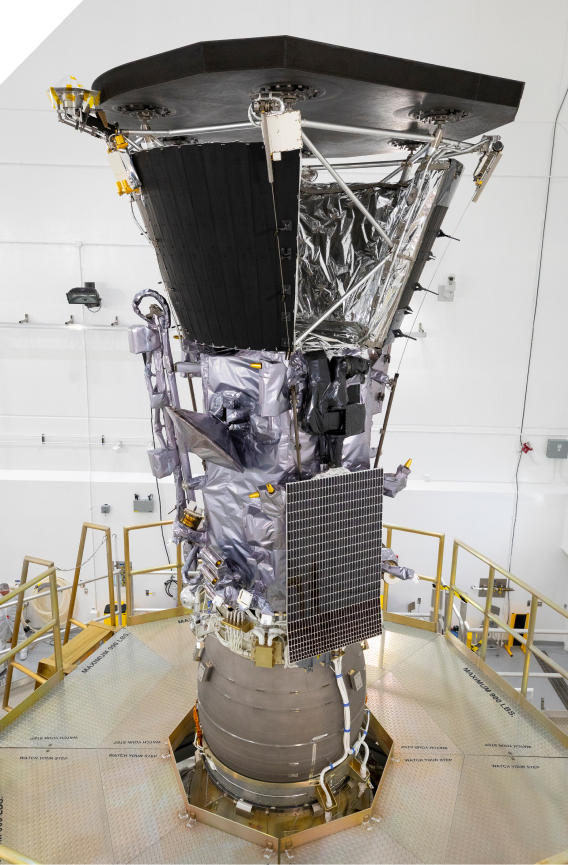

This lightweight insulation will be accompanied by a white ceramic coating finish on the sun-facing panel, to reflect as much heat as possible..But not all of the Solar Parker Probe instruments will be behind the TPS.
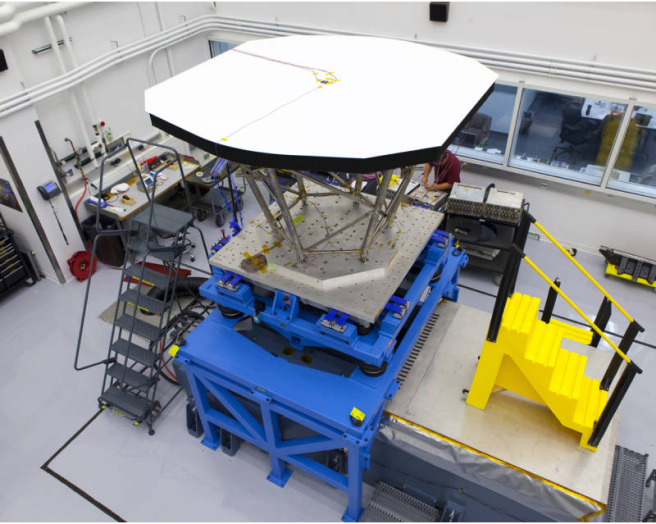

The Solar Probe Cup is one of two instruments on Parker Solar Probe that will not be protected by the heat shield. This instrument is what’s known as a Faraday cup, a sensor designed to measure the ion and electron fluxes and flow angles from the solar wind. Due to the intensity of the solar atmosphere, unique technologies had to be engineered to make sure that not only can the instrument survive, but also the electronics aboard can send back accurate readings.The cup itself is made from sheets of Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum, an alloy of molybdenum.The grids that produce an electric field for the Solar Probe Cup are made from tungsten, a metal with the highest known melting point of 6,192 F (3,422 C). Normally lasers are used to etch the gridlines in these grids — however due to the high melting point acid had to be used instead.Another challenge came in the form of the electronic wiring —most cables would melt from exposure to heat radiation at such close proximity to the Sun